Dr James Watson

Contact information
Podcast interview
Data driven definitions of severe malaria

James studies severe malaria in African children, focusing on improving diagnostic accuracy. By analysing clinical data, he aims to distinguish malaria-related severe illness from other infections and estimate true mortality more reliably. His work supports faster diagnosis and treatment, ultimately reducing preventable child deaths in low-resource settings.
Research groups
James Watson
IDDO Associate Director
Clinical Therapeutics
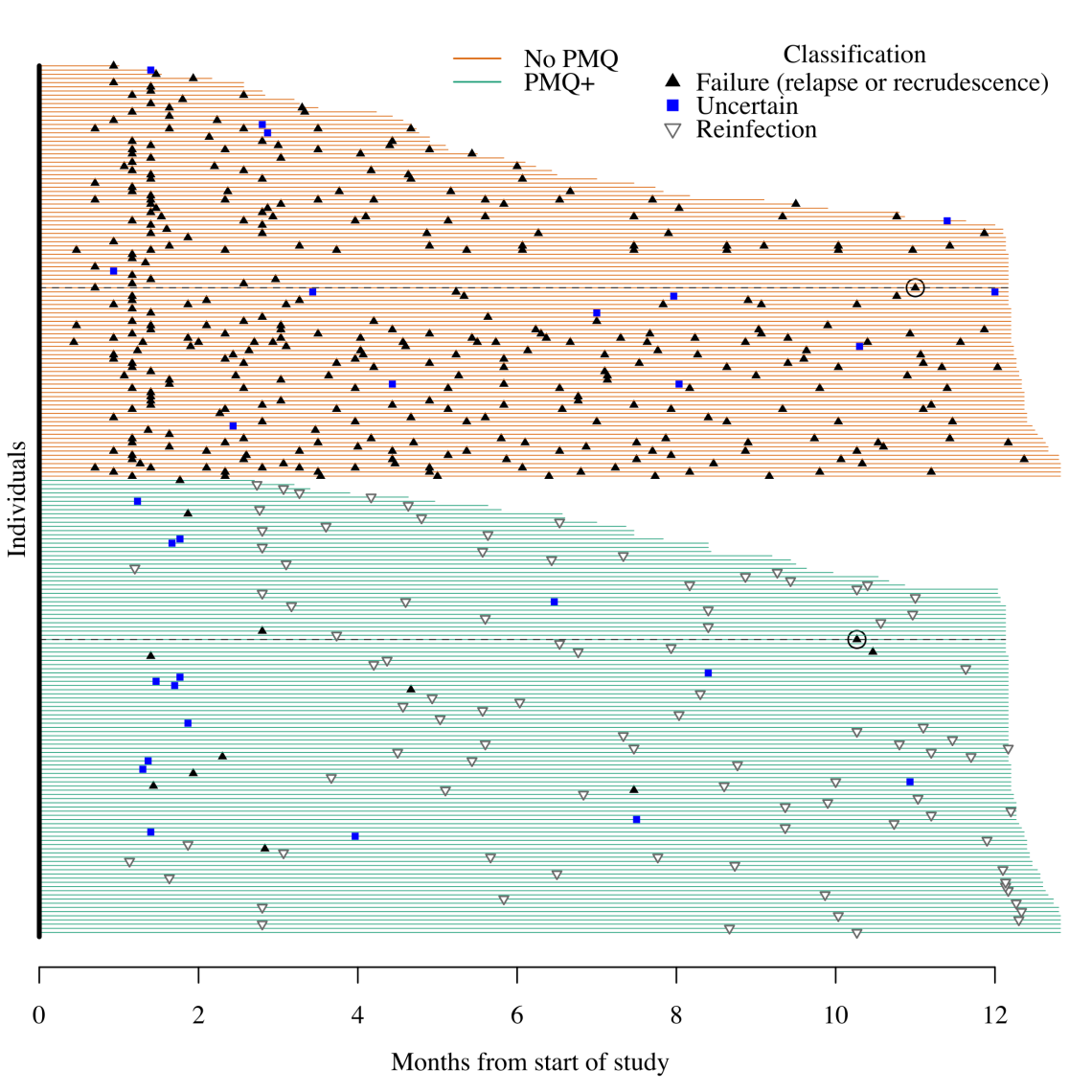
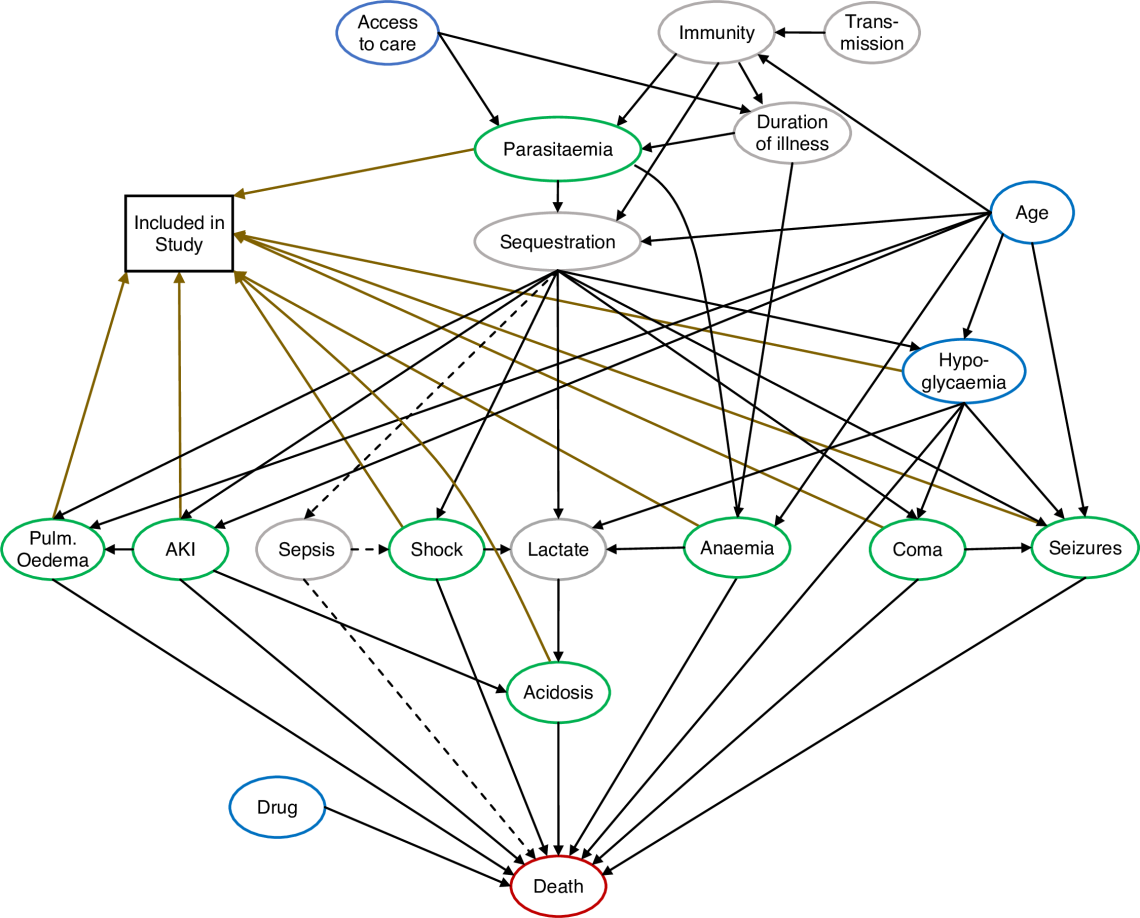
I am a statistician interested in improving the treatment of infectious diseases of global health importance. My main work focuses on severe malaria, notably improving the definition of severe malaria in areas of high malaria transmission. We have estimated that a third of children diagnosed with severe malaria in high transmission settings in fact have another cause of severe illness.
I also work on other infectious diseases: I am an investigator and study statistician for PLATCOV, a platform trial characterising in vivo antiviral effects of repurposed or novel drugs for COVID-19; I am an investigator on the CHARM project which aims to develop a new methodology for the assessment of new antiparasitic drugs for the treatment of Chagas disease.
Causal pathways in severe malaria
Recent publications
-
Accurate measurement of viral clearance in early phase antiviral studies in COVID-19.
Journal article
Wongnak P. et al, (2025), J Infect Dis
-
Characterising viral clearance kinetics in acute influenza
Preprint
Wongnak P. et al, (2025)
-
Tuberculosis preventive therapy: scientific and ethical considerations for trials of ultra-short regimens
Journal article
Walker TM. et al, (2025), The Lancet Infectious Diseases
-
Within-host modeling of primaquine-induced hemolysis in hemizygote glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient healthy volunteers.
Journal article
Watson JA. et al, (2025), Antimicrob Agents Chemother
-
Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)
Journal article
Jittamala P. et al, (2025), eClinicalMedicine, 80, 103036 - 103036